Let’s uncover the fascinating world of CAT scans and get a deeper understanding of what they truly are. A CAT scan, also known as a computerized axial tomography scan, is a modern medical imaging technology that provides detailed pictures of the inside of your body. By combining a series of X-ray images taken from different angles, a CAT scan creates a cross-sectional view of the body, allowing doctors to diagnose and monitor various health conditions with precision and accuracy. In this article, we will explore the benefits, process, and significance of CAT scans, unveiling the incredible impact they have on modern medicine.
Definition of a CAT Scan
Basic definition and full form of CAT Scan
A CAT scan, also known as CT scan (computed tomography), is a medical imaging procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. CAT stands for computerized axial tomography, which refers to the process of capturing images from different angles around the body and then using a computer to reconstruct them into a 3D view.
Brief history of the CAT Scan technology
The development of CAT scan technology can be traced back to the early 1970s when the first commercially available CT scanner was introduced. The inventors, Sir Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack, revolutionized medical imaging by creating a device that could produce detailed images of internal structures of the body. Since then, CAT scans have become an essential tool in modern medicine for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of health conditions.
How CAT Scan Works
The role of X-rays in CAT Scans
X-rays play a crucial role in CAT scans. The X-ray machine emits a series of narrow beams of radiation that pass through the body from different angles. As the X-rays penetrate the body, they are absorbed by different types of tissues to varying degrees. The X-ray detector on the opposite side of the body measures the amount of radiation that passes through.
The circular rotation of the X-ray machine
To capture images from multiple angles, the X-ray machine rotates around the patient’s body during a CAT scan. It completes a full circle or rotation, capturing numerous X-ray images along the way. These images are then processed by a computer to create a cross-sectional view of the scanned area.
The creation of cross-sectional images
The computer takes the raw data collected from the X-ray images and uses a complex mathematical algorithm to reconstruct the information into cross-sectional images. These images provide detailed visualizations of the internal structures, allowing healthcare professionals to examine organs, bones, and tissues from various angles.
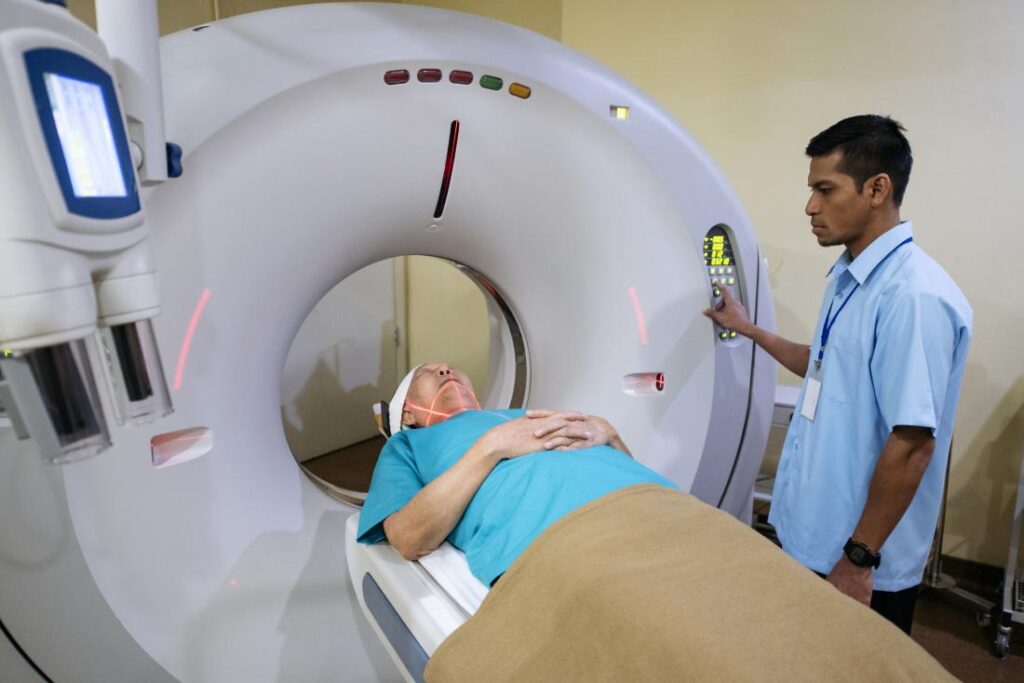
The Preparation Process for a CAT Scan
Preparation instructions for patients
Prior to a CAT scan, patients may be given specific instructions to prepare for the procedure. These instructions typically include fasting for a certain period, depending on the type of scan being performed. Patients may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan to ensure accurate results.
The use of contrast dye
In some cases, a contrast dye may be administered to enhance the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels during a CAT scan. The dye is usually given orally, injected, or administered through an enema, depending on the area being scanned. Patients with allergies or other health conditions should inform their healthcare provider beforehand.
Potential restrictions prior to the scan
Patients may be advised to avoid wearing any metal objects, such as jewelry or clothing with metal fastenings, as they can interfere with the scanning process. Additionally, pregnant women or individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney problems, may need to discuss the risks and benefits of a CAT scan with their healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
The Procedure of a CAT Scan
How patients are positioned for a CAT Scan
During a CAT scan, patients are positioned on a movable examination table. The table is then carefully aligned with the scanner’s opening, ensuring the area of interest is in the center of the machine. Depending on the type of scan, patients may be asked to lie still in one position or may need to change positions during the scan.
Length and stages of a common CAT Scan
The length of a CAT scan procedure can vary depending on the areas being examined and the complexity of the case. Typically, a CAT scan takes only a few minutes to complete. However, the process may involve several stages, including the initial positioning, obtaining the images from different angles, and reviewing the images for quality and accuracy before the patient is removed from the scanner.
The role of radiologists and radiologic technologists
CAT scans are conducted and supervised by healthcare professionals specializing in radiology, such as radiologists and radiologic technologists. Radiologists interpret the images generated by the CAT scan and provide diagnostic reports to the referring healthcare provider. Radiologic technologists operate the CAT scan equipment and ensure the patient’s safety and comfort during the procedure.
Types of CAT Scans
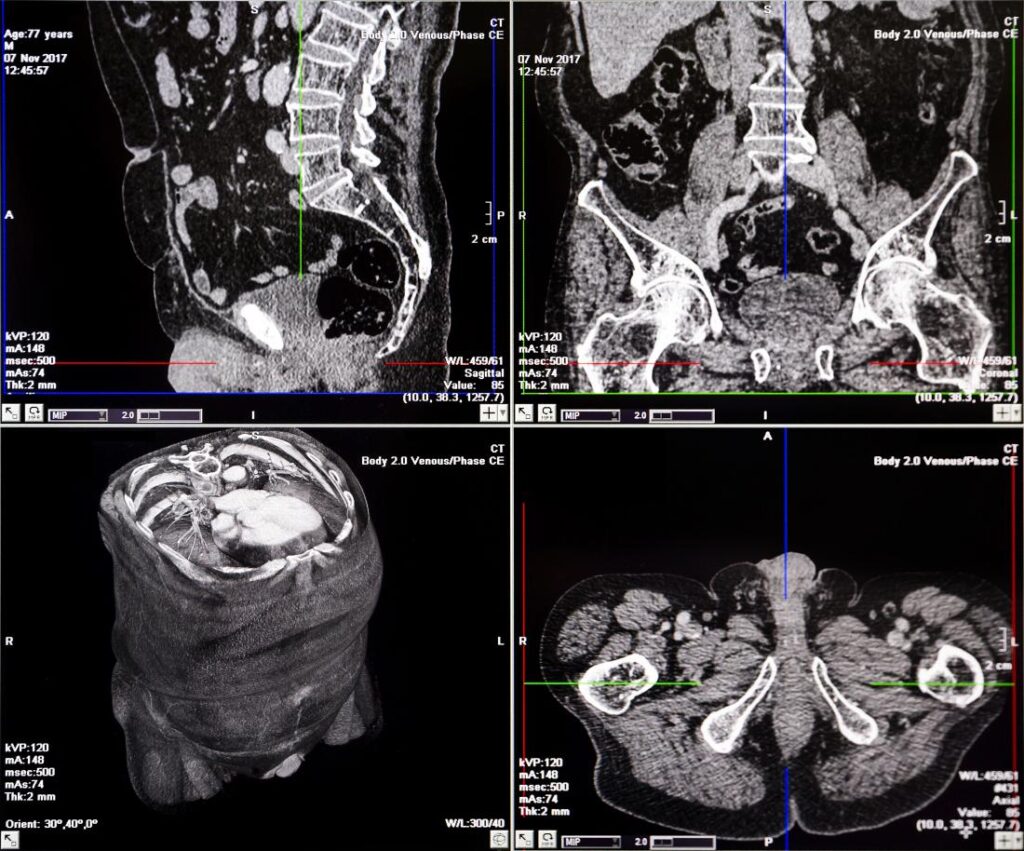
Abdominal and Pelvic CAT Scans
Abdominal and pelvic CAT scans produce detailed images of the organs within the abdominal and pelvic regions, such as the liver, kidneys, bladder, and reproductive organs. These scans help diagnose conditions like tumors, infections, kidney stones, and appendicitis, and assist in planning surgical interventions.
CAT Scans for the brain
CAT scans of the brain, also known as cranial CT scans, provide valuable information about the brain’s structure and possible abnormalities. They are commonly used to detect and evaluate brain tumors, hemorrhages, stroke, brain injuries, and other conditions affecting the brain.
Chest CAT Scans
Chest CAT scans focus on capturing detailed images of the organs within the chest cavity, including the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. These scans help diagnose conditions such as lung cancer, pneumonia, heart disease, and pulmonary embolism.
CAT Scans for lungs and heart
Specifically dedicated to the lungs and heart, CAT scans can detect pulmonary nodules, lung diseases, blood clots in the pulmonary arteries, and heart abnormalities. They provide a clear view of these vital structures, helping healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses and determine appropriate treatment plans.
Interpreting CAT Scan Results
The role of radiologists in interpretation
Radiologists are specialized physicians trained to interpret CAT scan images accurately. They analyze the cross-sectional images obtained from the scan to identify any abnormalities or areas of concern. They also compare the results with previous scans, if available, to track changes over time and assist in providing a proper diagnosis.
Expected time for results
The time it takes for CAT scan results to be available can vary. In urgent cases, preliminary results may be provided immediately to help guide immediate medical interventions. In non-urgent cases, it may take several hours or days for the radiologist to thoroughly analyze the images and provide a detailed report to the healthcare provider responsible for the patient’s care.
How results are communicated to patients
Typically, the CAT scan results are communicated to the patients through their healthcare provider. The provider will review the radiologist’s report and discuss the findings, any abnormalities, and potential treatment options with the patient. They will answer any questions or concerns the patient may have and develop a plan for further care based on the results.
Risks and Side Effects of CAT Scans
Possible exposure to radiation
One of the primary concerns regarding CAT scans is the potential exposure to radiation. While the radiation doses used in modern CAT scans are considered safe, repeated exposure to radiation may increase the risk of certain cancers. However, the benefits of accurate diagnosis and timely treatment often outweigh the minimal risks associated with radiation exposure for most patients.
Reactions to contrast dye
In some cases, patients may experience allergic reactions to the contrast dye used during a CAT scan. These reactions can range from mild skin rashes to more severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis. Patients with a known allergy to contrast dye or a history of allergic reactions should inform their healthcare provider before the procedure.
Potential complications for patients with certain health conditions
Patients with pre-existing kidney problems may be at a higher risk of developing complications due to the contrast dye used in the CAT scan. The dye can cause a temporary decline in kidney function or, in rare cases, lead to more severe conditions. Healthcare providers carefully assess any potential risks before administering contrast dye to patients with kidney impairments.
Benefits of CAT Scans
Ability to detect various health issues
CAT scans have the ability to detect a wide range of health conditions, including tumors, infections, injuries, and abnormalities in the organs and tissues. The detailed cross-sectional images allow healthcare providers to accurately diagnose these conditions and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Benefits over other imaging techniques
Compared to other imaging techniques like X-rays or ultrasound, CAT scans offer superior detail and accuracy in capturing internal structures. The cross-sectional images produced by CAT scans provide a comprehensive view, making it easier for healthcare providers to identify and locate abnormalities or structures of interest.
Ability to guide treatments
CAT scans play a crucial role in guiding treatments. They help surgeons plan surgical procedures by providing precise details of a patient’s anatomy. During procedures, CAT scans allow real-time monitoring and guidance, enhancing precision and reducing the risks associated with certain interventions.
Common Questions and Misconceptions about CAT Scans
Difference between CAT Scan and MRI
One common question is the difference between a CAT scan and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). While both are medical imaging techniques, they work on different principles. CAT scans use X-rays and provide detailed images of bones, organs, and tissues, while MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues, such as the brain, muscles, and joints.
Questions about safety and radiation exposure
Many individuals wonder about the safety of CAT scans and the potential risk of radiation exposure. It is essential to understand that CAT scans use low doses of radiation, and the benefits of accurate diagnosis often outweigh the risks associated with radiation exposure. However, healthcare providers take every precaution to minimize radiation doses, especially in children and pregnant women, while still ensuring the accuracy of the scan.
Common misconceptions regarding CAT Scans
There are a few common misconceptions about CAT scans that can cause unnecessary concerns. Some individuals believe that CAT scans are painful or that they involve inserting needles or tubes into the body. However, CAT scans are painless procedures that only require the patient to lie still on the examination table while the scanner rotates around them.
Advancements in CAT Scan Technology
The advent of spiral or helical CAT Scans
Spiral or helical CAT scans represent a significant advancement in scanning technology. Instead of a single rotation, this technique allows the scanner to move continuously in a spiral motion while capturing images. This results in faster scans, reduced motion artifacts, and improved image quality.
Development of multi-detector CAT Scan
Multi-detector CAT scans, also known as MDCT, utilize an array of detectors to simultaneously capture multiple slices of data during a single rotation. This technology drastically reduces the scan time and provides even more detailed images, allowing for better visualization of complex structures and faster diagnosis.
The future of CAT Scan technology
As technology continues to evolve, CAT scan technology is expected to advance further. Future innovations may focus on improving image resolution, reducing radiation doses, and enhancing the efficiency of the scanning process. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms may also improve diagnostic accuracy and assist in image analysis.
In conclusion, CAT scans play a vital role in modern medicine, allowing healthcare professionals to obtain detailed cross-sectional images of the body. With its ability to diagnose various health conditions, guide treatments, and provide valuable insights, CAT scans have become an indispensable tool in medical imaging. By understanding the procedure, risks, benefits, and advancements in CAT scan technology, patients can feel more informed and confident when undergoing this important diagnostic procedure.